Rituximab Off-Label Adoption for Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (2000s)
2001-2015What Happened
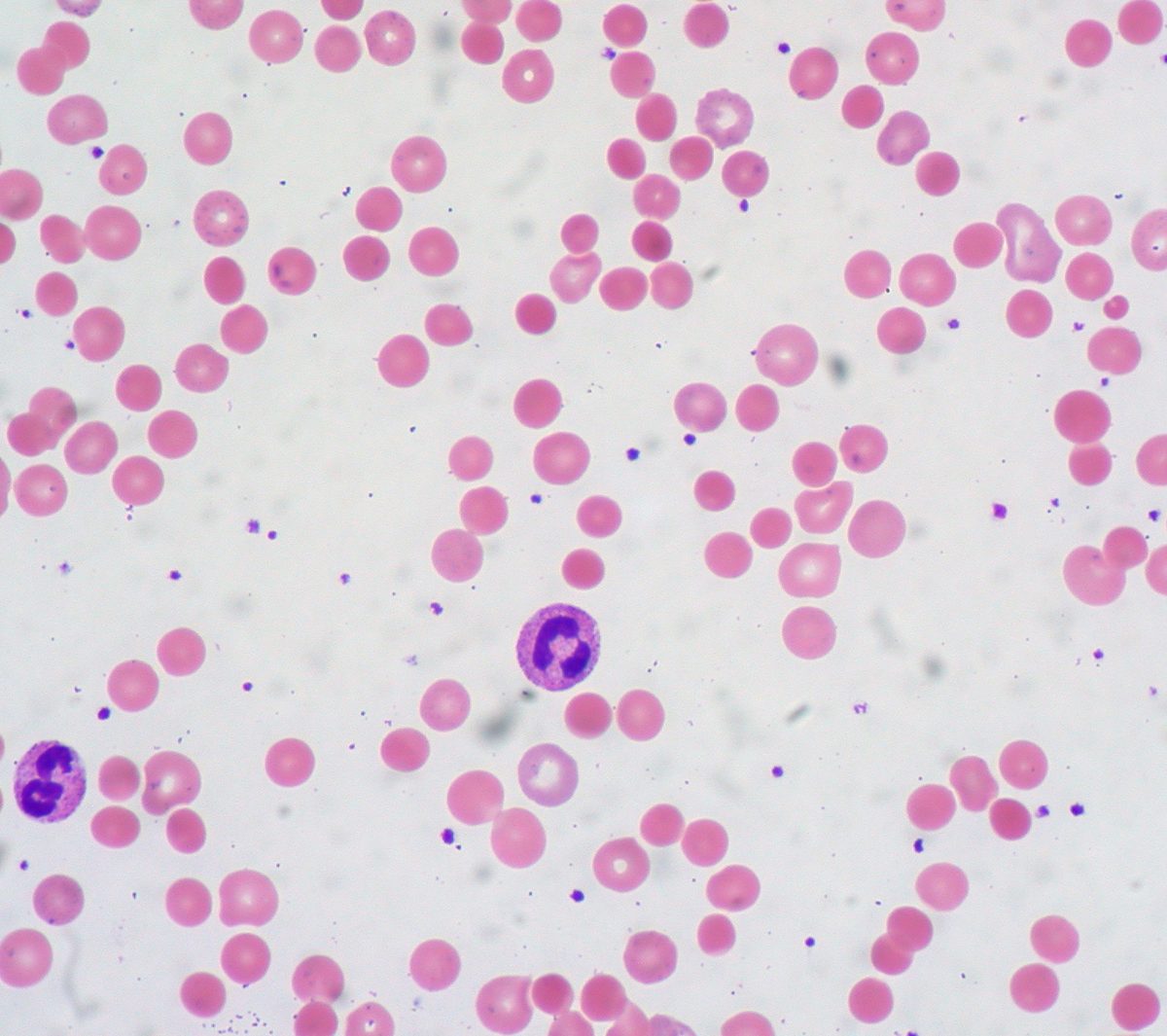
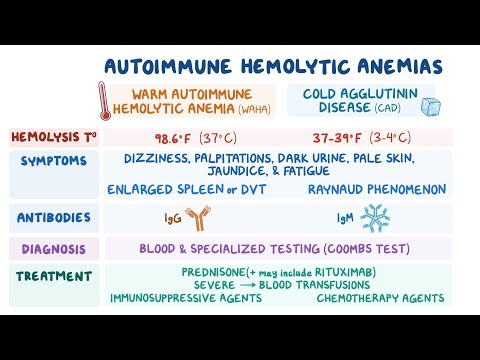
Rituximab, originally approved for non-Hodgkin lymphoma in 1997, began showing efficacy in autoimmune hemolytic anemia through case reports and small studies. Physicians adopted it off-label for steroid-refractory patients, achieving 70-80% response rates. Despite widespread use, no manufacturer pursued a formal FDA approval for this indication.
Outcome
Rituximab became the de facto second-line therapy for wAIHA worldwide, despite lacking FDA approval for this use.
The pattern demonstrated how rare disease patients rely on off-label treatments when no approved therapies exist. It also showed pharmaceutical companies rarely invest in approval studies for small patient populations without financial incentives.
Why It's Relevant Today
Rilzabrutinib's path illustrates a potential shift: orphan drug incentives and breakthrough therapy pathways now make rare autoimmune conditions commercially viable targets. If approved, it would be the first treatment specifically developed and approved for wAIHA.