The Great Divergence (1820-1980)
1820-1980What Happened
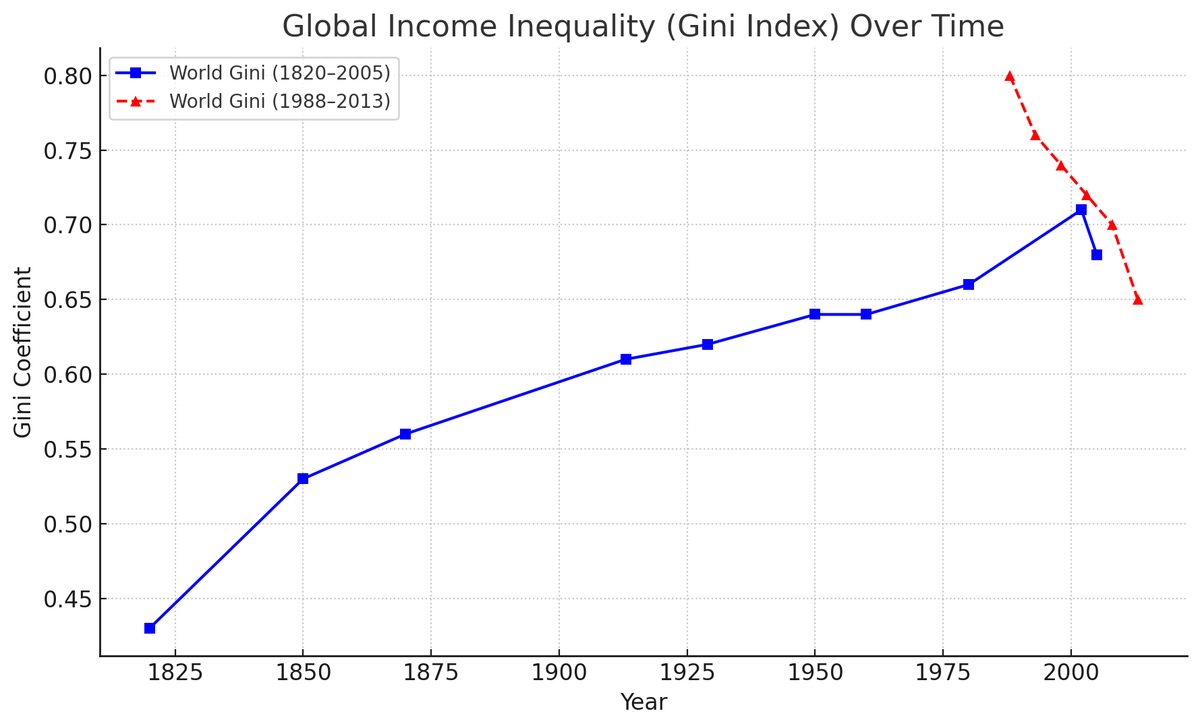
The Industrial Revolution concentrated economic growth in Western Europe and North America. Britain, then the US, pulled away from the rest of the world. By 1980, Western countries controlled two-thirds of global income despite comprising a fraction of world population. The global Gini rose from 0.50 to 0.70.
Outcome
Living standards in industrialized countries rose dramatically while most of Asia and Africa remained subsistence economies.
Created the 'developed' vs 'developing' world division that persisted until the 1990s. Established the baseline from which current convergence is measured.
Why It's Relevant Today
The current decline in global inequality is a reversal of this 160-year trend—the first sustained movement toward equality since industrialization began.