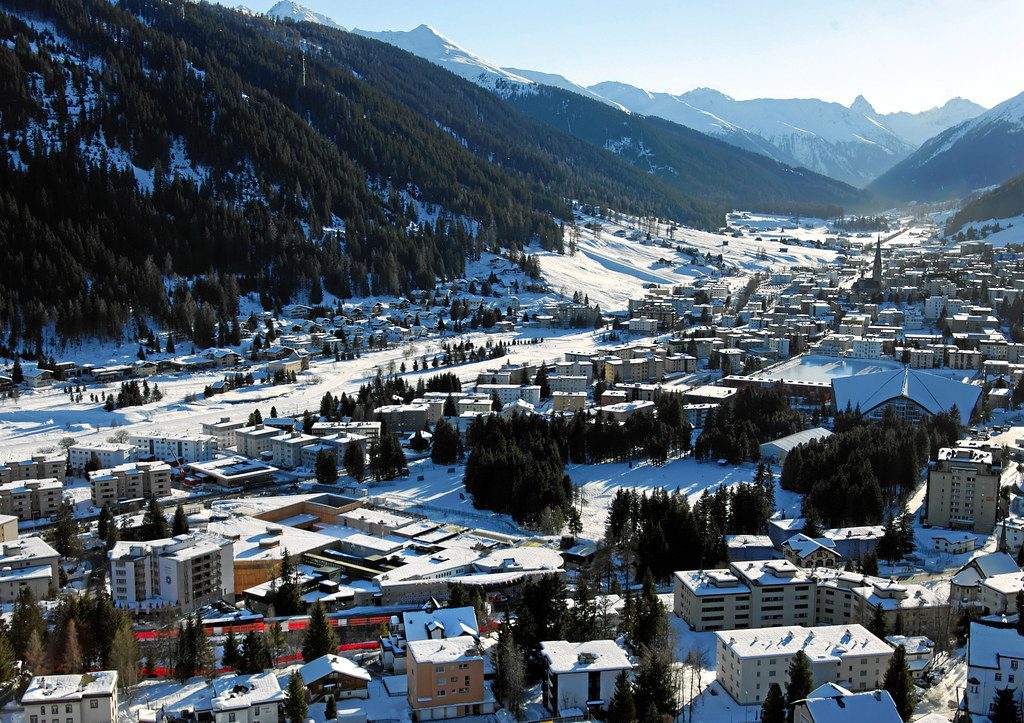
Davos Declaration Between Greece and Turkey (1988)
January 1988What Happened
Greek PM Andreas Papandreou and Turkish PM Turgut Özal met at Davos during an acute crisis that had brought their countries to the brink of war over Aegean territorial disputes. The forum provided neutral ground for direct dialogue.
Outcome
The leaders signed the Davos Declaration, establishing direct communication channels and stepping back from military confrontation.
Set precedent for WEF as venue for crisis diplomacy. Greece-Turkey tensions continued but the 1988 war was averted.
Why It's Relevant Today
Davos 2026 similarly became an emergency diplomatic venue, with the Greenland crisis transforming scheduled programming into high-stakes negotiations between Trump and European leaders.